# Image Classification and ML in Disease Recognition: A Research Review
**Medical ML Research Series**
**By Oleh Ivchenko, PhD Candidate**
**Affiliation:** Odessa Polytechnic National University | Stabilarity Hub | February 2026
—
—
## Introduction
**Medical image analysis stands at a transformative crossroads.** As deep learning models achieve remarkable accuracy in disease detection, a critical question emerges: how do we integrate AI into clinical workflows to maximize diagnostic accuracy while minimizing errors? This comprehensive review examines the current state of ML in medical imaging, mapping which techniques apply at each diagnostic stage, and synthesizing evidence-based best practices for human-AI collaboration.
—
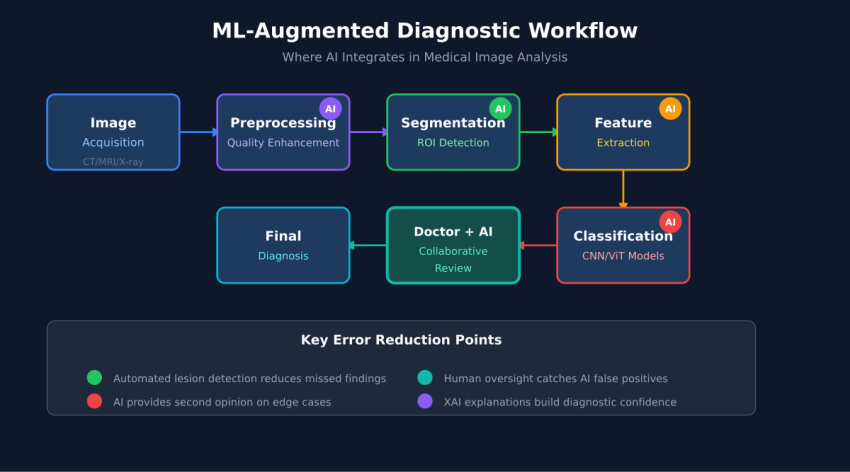
## The Medical Image Analysis Pipeline
—
## ML Model Evolution
—
## Case Studies: Performance Metrics
🔬 Skin Cancer Detection
94.4%
EViT-DenseNet169 on HAM10000
Hybrid attention + multi-scale fusion
🔬 Breast Cancer
92%
Self-Attention CNN + GA
Inverted residual blocks + feature selection
🔬 Diabetic Retinopathy
97%
Vision Transformer
Global context attention
—
## Doctor-AI Collaboration Framework
—
## Tiered Review Protocol
—
## ML Architectures by Disease Domain
—
## Unique Conclusions
🔬 Conclusion 1: The Heterogeneity Paradox
Physician experience does not predict who benefits most from AI assistance. Universal deployment with individualized feedback is more effective than experience-based targeting.
🔬 Conclusion 2: The Hybrid Architecture Advantage
Across disease domains, hybrid CNN-Transformer architectures consistently outperform pure approaches. CNNs excel at local features while Transformers capture global context.
🔬 Conclusion 3: Adaptive Explainability
Optimal solution is adaptive explainability: detailed explanations only when AI-physician disagreement occurs or confidence is low.
—
## References
1. Ly, N. et al. “Recent Advances in Medical Image Classification.” arXiv:2506.04129, 2025.
2. Agarwal, N. et al. “Heterogeneity and predictors of AI effects on radiologists.” *Nature Medicine*, 2024.
3. Chen, R.J. et al. “A pathologist–AI collaboration framework.” *Nature Biomedical Engineering*, 2024.
4. “Enhanced early skin cancer detection through EViT-DenseNet169.” *Scientific Reports*, 2025.
5. “Artificial intelligence based classification using inverted self-attention DNN.” *Scientific Reports*, 2025.
—
**Author:** Oleh Ivchenko, PhD Candidate
**Affiliation:** Odessa Polytechnic National University | Stabilarity Hub